

Don’t be afraid to interrogate the person submitting the sample. Thus, it is useful to have other information about a sample in addition to its IR spectrum. Step 3: Use Other Knowledge of the Sample An IR spectrum contains a lot of information about a sample, but by itself will not necessarily tell you everything you need to know about a sample. Please consult that installment for guidance on this topic.
IR INTERPRETATION CHART HOW TO
A large part of a previous column was devoted to how to get around the mixture analysis problem (2). The problem with mixtures in IR spectroscopy is that the more complex the composition of a sample, the more difficult it becomes to figure out what peaks are from what functional groups. For more on spectral quality and how to fix spectral problems see my book on Fourier transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopy (1). This is the type of spectrum you should be interpreting. The baseline is flat and close to zero, the peaks are on scale, and there are no spectral artifacts. There is little fuzz in the baseline, meaning the spectrum is low noise.
IR INTERPRETATION CHART FREE
It has low noise, little baseline offset, a flat baseline, the peaks are on scale, and it is free of spectral artifacts. These peaks can be minimized by running a fresh background, changing the desiccant in your instrument, or purging the instrument with dry nitrogen.įigure 2 is an example of a good IR spectrum.įigure 2: An example of a good IR spectrum. The most common types of spectral artifacts in IR spectra are water vapor and CO 2 peaks a CO 2 peak is shown in Figure 1. Spectral artifacts are peaks not caused by the sample. If the peaks are outside these ranges and thus off scale, reduce the pathlength or concentration of the sample. The peaks in an IR spectrum should be between 0 and 2 absorbance units, or 10% to 90% transmittance. If that doesn’t work, re-prepare the sample. If it is not, try running a fresh background spectrum and then running your sample again. Ideally, the baseline should be as close to zero as possible. Offset is a measure of how far the spectral baseline is away from zero.

Noise is represented by fuzz in the baseline as indicated. Note the high noise, offset, sloped baseline, and presence of a CO 2 artifact peak. If the noise is too large you may need to do more scans or re-prepare the sample.įigure 1: An example of a bad IR spectrum. Learn to eyeball the noise level in your spectra by looking at the amount of noise seen as “fuzz” in the baseline as indicated in Figure 1. There are at least five attributes of a good spectrum: low noise, little or no baseline offset, a flat baseline, peaks on scale, and a lack of spectral artifacts.Īn example of a bad spectrum is shown in Figure 1. The higher the quality of the spectrum you are working with, the easier your interpretation job will be. This column will teach you a 12-step program that, if followed, should help you be more successful at interpreting spectra. To successfully interpret infrared spectra one must follow the right process, or else it is easy to be misled. The challenge with interpreting spectra, however, is that with the hundreds of known functional groups that absorb in the mid-infrared and the resultant thousands of peaks, it becomes difficult to figure out what peaks are from what functional groups. Infrared (IR) spectral interpretation is firmly grounded in science as seen in the theory sections in previous installments.

The answer to last column’s quiz is also disclosed.
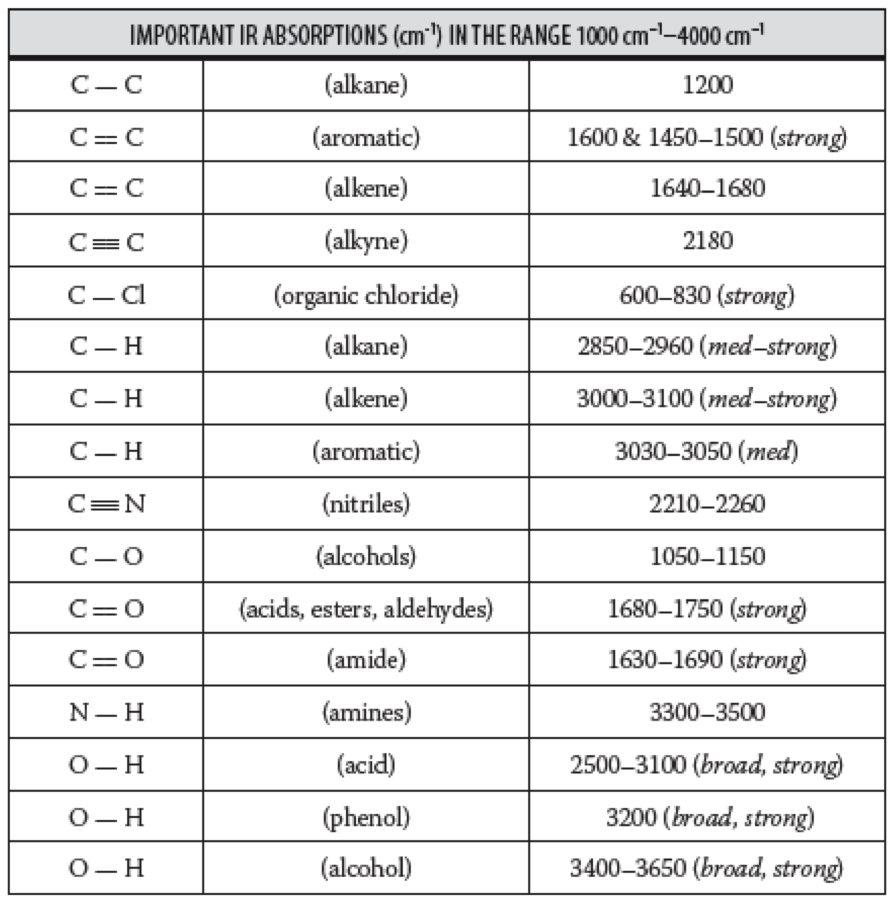
The process includes knowing how a spectrum was measured, systematically identifying peaks, and the proper use of infrared spectral interpretation aids. The author has developed this 12-step system over many years of interpreting spectra, and finds it gives him the best results. We wrap up our introduction to the theory of infrared spectral interpretation with a discussion of the correct process to follow when interpreting spectra.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
