
The detachment appears round/ convex with hyperpigmentation and/or retinal vessels at the summit of the retinal detachment.Retinal connective tissue membranes and/or connective tissue proliferation in the papilla region.The detached retina appears tented and is relatively immobile.
 Non- rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: No retinal tear is observed. Old retinal detachments: retinal thinning, subretinal demarcation line ( high-water mark), secondary intraretinal cysts. Blood-vessel orientation in the detached portion of the retina differs from that in the normal retina. The detached retina floats freely in the vitreous body, and moves with eye movements. A retinal tear may potentially be visible (e.g., horseshoe, linear, or round retinal tears). Opthalmoscopic findings: A freshly detached retina has a grey color instead of the normal pink color and may appear crinkled. Indirect retinoscopy is useful to visualize the peripheral retina. References: Pathophysiologyīoth direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy should be performed after dilating the pupil. Sudden decrease in intra-ocular pressure due to perforating injuries or intraocular surgery. Scar tissue following penetrating injury. Peripheral retinal breaks, commonly due to:. Previous intraocular surgery (e.g., cataract surgery). Subretinal fluid accumulation without retinal tears. Formation of vitreoretinal bands → traction on the vitreoretinal band during eye movements or as a result of sudden decrease in intraocular pressure → retinal detachment. Retinal tears → retinal fluid, which is formed by vitreous degeneration, seeps into the subretinal space → retinal detachment. Visual prognosis depends particularly on the extent of retinal detachment (poor with macular involvement) and how much time passes before the retina is reattached. Extensive retinal detachment is an ophthalmic emergency and usually requires prompt surgery to prevent further detachment and restore sensory function. To prevent retinal detachment, laser photocoagulation in the direct vicinity of the retinal defect should be performed after diagnosis of retinal tears or holes. The diagnosis is confirmed by ophthalmoscopy. Loss of vision may be severe if the retinal detachment is extensive and/or the macula is affected. Small detachments typically present with photopsia, floaters, and/or visual field defects. Non-rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is most often the result of vitreoretinal bands (e.g., proliferative diabetic retinopathy), subretinal/intraretinal tumors (e.g., choroidal melanoma), or a number of systemic and ocular causes that result in subretinal fluid accumulation. Less commonly, retinal detachment occurs without any retinal tears ( non-rhegmatogenous retinal detachment). The most frequent causes of retinal detachment are tears or holes in the retina ( rhegmatogenous retinal detachment), risk factors for which include myopia, previous intraocular surgery, trauma, and/or posterior vitreous detachment. U.S.Retinal detachment refers to the detachment of the inner layer of the retina (neurosensory retina) from the retinal pigment epithelium. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. After a successful procedure, vision will take time to improve but may not return to previous levels of acuity. In some cases, a second procedure will need to be performed. Most surgeries to repair a retinal detachment are successful. Diagnosis of a Retinal Detachmentĭiagnosis of a retinal detachment is made after a thorough medical eye examination and the performance of the following diagnostic tests:Ī retinal detachment may be treated in many ways, which may include one or both of the following: The patient should be taken to an emergency room as quickly as possible. A dense shadow throughout the visual field. An unnatural "curving" of straight lines. A sudden increase in the amount of "floaters" in vision. Some of the symptoms of a retinal detachment include: Symptoms of retinal detachment may progress slowly or rapidly, but both should be reported to a medical doctor as soon as possible so as to minimize the risk of vision loss. Other causes of a retinal detachment may be as follows:
Non- rhegmatogenous retinal detachment: No retinal tear is observed. Old retinal detachments: retinal thinning, subretinal demarcation line ( high-water mark), secondary intraretinal cysts. Blood-vessel orientation in the detached portion of the retina differs from that in the normal retina. The detached retina floats freely in the vitreous body, and moves with eye movements. A retinal tear may potentially be visible (e.g., horseshoe, linear, or round retinal tears). Opthalmoscopic findings: A freshly detached retina has a grey color instead of the normal pink color and may appear crinkled. Indirect retinoscopy is useful to visualize the peripheral retina. References: Pathophysiologyīoth direct and indirect ophthalmoscopy should be performed after dilating the pupil. Sudden decrease in intra-ocular pressure due to perforating injuries or intraocular surgery. Scar tissue following penetrating injury. Peripheral retinal breaks, commonly due to:. Previous intraocular surgery (e.g., cataract surgery). Subretinal fluid accumulation without retinal tears. Formation of vitreoretinal bands → traction on the vitreoretinal band during eye movements or as a result of sudden decrease in intraocular pressure → retinal detachment. Retinal tears → retinal fluid, which is formed by vitreous degeneration, seeps into the subretinal space → retinal detachment. Visual prognosis depends particularly on the extent of retinal detachment (poor with macular involvement) and how much time passes before the retina is reattached. Extensive retinal detachment is an ophthalmic emergency and usually requires prompt surgery to prevent further detachment and restore sensory function. To prevent retinal detachment, laser photocoagulation in the direct vicinity of the retinal defect should be performed after diagnosis of retinal tears or holes. The diagnosis is confirmed by ophthalmoscopy. Loss of vision may be severe if the retinal detachment is extensive and/or the macula is affected. Small detachments typically present with photopsia, floaters, and/or visual field defects. Non-rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is most often the result of vitreoretinal bands (e.g., proliferative diabetic retinopathy), subretinal/intraretinal tumors (e.g., choroidal melanoma), or a number of systemic and ocular causes that result in subretinal fluid accumulation. Less commonly, retinal detachment occurs without any retinal tears ( non-rhegmatogenous retinal detachment). The most frequent causes of retinal detachment are tears or holes in the retina ( rhegmatogenous retinal detachment), risk factors for which include myopia, previous intraocular surgery, trauma, and/or posterior vitreous detachment. U.S.Retinal detachment refers to the detachment of the inner layer of the retina (neurosensory retina) from the retinal pigment epithelium. Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. After a successful procedure, vision will take time to improve but may not return to previous levels of acuity. In some cases, a second procedure will need to be performed. Most surgeries to repair a retinal detachment are successful. Diagnosis of a Retinal Detachmentĭiagnosis of a retinal detachment is made after a thorough medical eye examination and the performance of the following diagnostic tests:Ī retinal detachment may be treated in many ways, which may include one or both of the following: The patient should be taken to an emergency room as quickly as possible. A dense shadow throughout the visual field. An unnatural "curving" of straight lines. A sudden increase in the amount of "floaters" in vision. Some of the symptoms of a retinal detachment include: Symptoms of retinal detachment may progress slowly or rapidly, but both should be reported to a medical doctor as soon as possible so as to minimize the risk of vision loss. Other causes of a retinal detachment may be as follows: 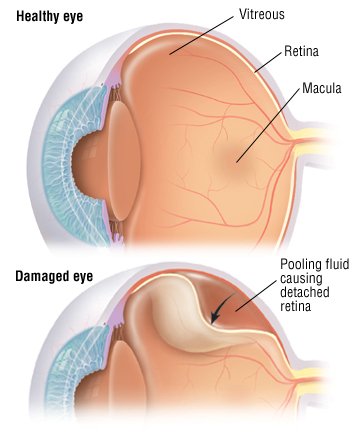
A severe inflammation may alter the position of the retinal tissue and begin the detachment process.
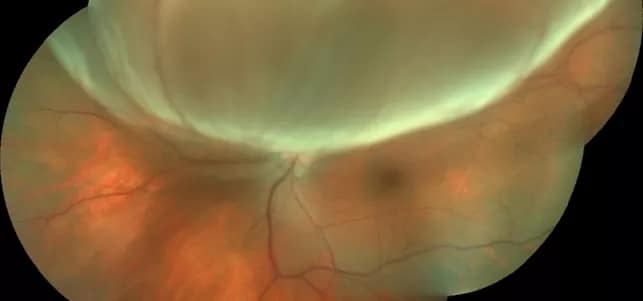
Retinal detachment can be complication of cataract surgery. In some cases, a detachment occurs due to a trauma which causes a tear in the retina, allowing fluid to enter the vitreous and pull on the retinal tissue. In most cases, the detachment is a slowly progressing issue which must be treated once symptoms are realized. A retinal detachment is a medical emergency which can lead to permanent blindness if left untreated. Retinal detachment occurs when the retina of the eye is pulled away from the underlying tissue to which it is attached.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
